The x86 Memory
This will be a very brief explanation of how the memory works in a program.
This is how the memory layout looks like in a program:
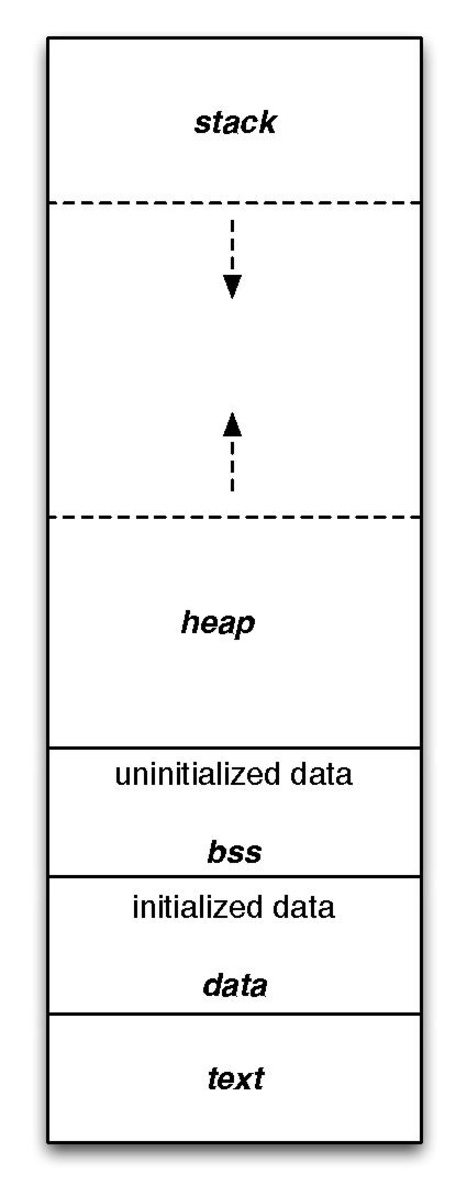
Let’s get straight to our example
Example
Consider the following program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
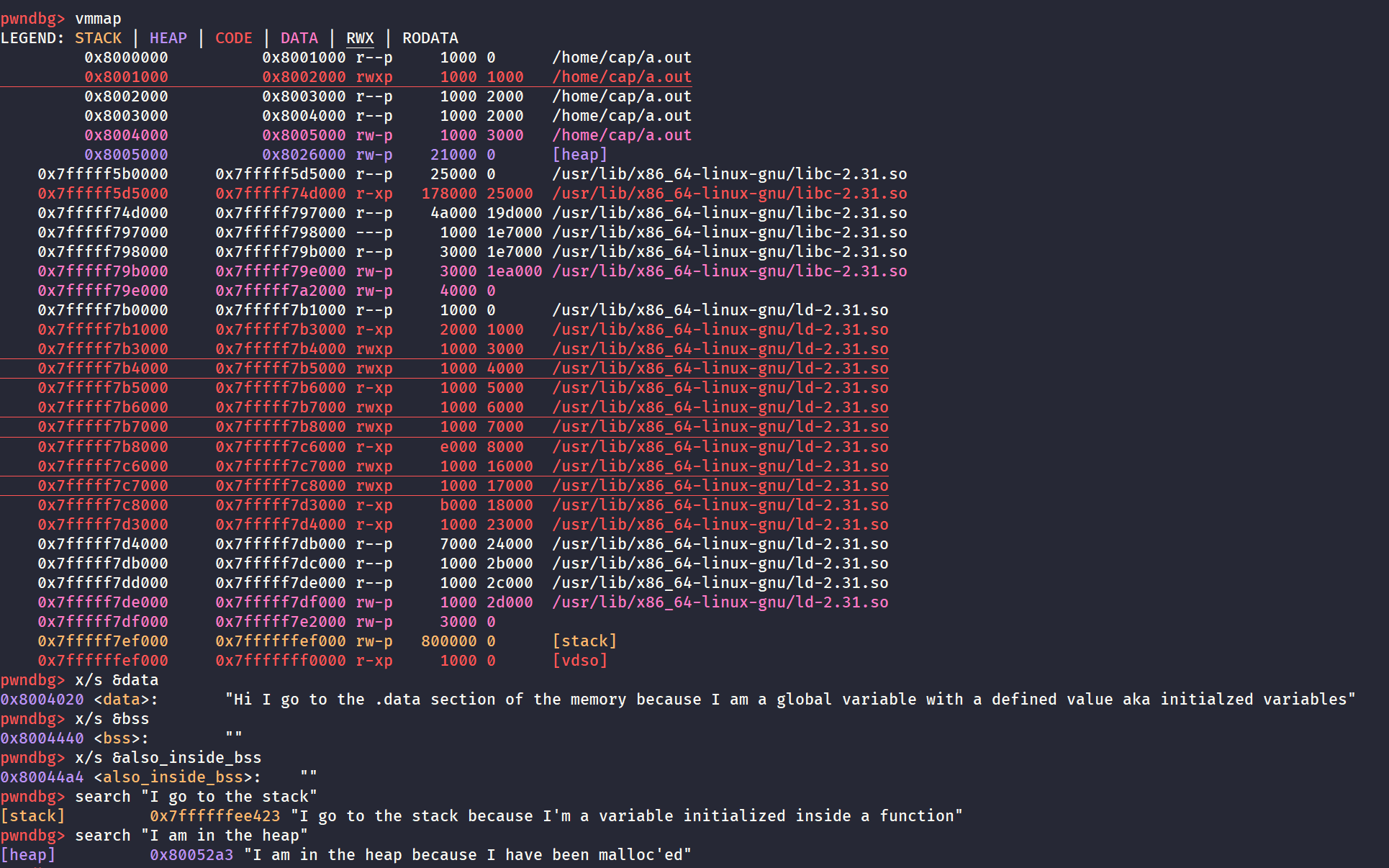
char data[1000] = "Hi I go to the .data section of the memory because I am a global variable with a defined value aka initialzed variables";
char bss[100];
int also_inside_bss;
// These 2 variables are in the bss section of the memory because they are global variables with no defined values aka uninitialised variables
void main() {
char hello[100] = "Hi I go to the stack because I'm a variable initialized inside a function";
char *heap;
heap = malloc(100);
strcpy(heap, "Hi I am in the heap because I have been malloc'ed");
}
And this is how it all comes together!
comments powered by Disqus